What is a DC motor?
A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. In a DC motor, the input electrical energy is the direct current which is transformed into the mechanical rotation.
Definition of DC motor
A DC motor is defined as a class of electrical motors that convert direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy.
From the above definition, we can conclude that any electric motor that is operated using direct current or DC is called a DC motor. We will understand the DC motor construction and how a DC motor converts the supplied DC electrical energy into mechanical energy in the next few sections.
DC Motor Parts
In this section, we will be discussing the construction of DC motors.
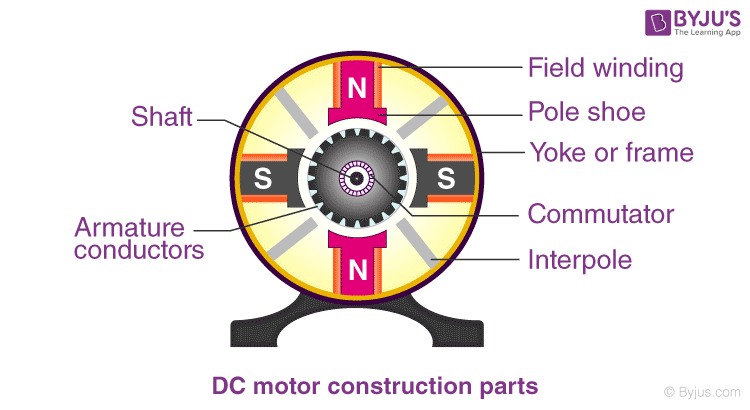
DC Motor Diagram
Different Parts of a DC motor
A DC motor is composed of the following main parts::
Armature or Rotor
The armature of a DC motor is a cylinder of magnetic laminations that are insulated from one another. The armature is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder. The armature is a rotating part that rotates on its axis and is separated from the field coil by an air gap.
Field Coil or Stator
A DC motor field coil is a non-moving part on which winding is wound to produce a magnetic field. This electro-magnet has a cylindrical cavity between its poles.
Commutator and Brushes
Commutator
The commutator of a DC motor is a cylindrical structure that is made of copper segments stacked together but insulated from each other using mica. The primary function of a commutator is to supply electrical current to the armature winding.
Brushes
The brushes of a DC motor are made with graphite and carbon structure. These brushes conduct electric current from the external circuit to the rotating commutator. Hence, we come to understand that the commutator and the brush unit are concerned with transmitting the power from the static electrical circuit to the mechanically rotating region or the rotor.
DC Motor Working Explained
In the previous section, we discussed the various components of a DC motor. Now, using this knowledge let us understand the working of DC motors.
A magnetic field arises in the air gap when the field coil of the DC motor is energised. The created magnetic field is in the direction of the radii of the armature. The magnetic field enters the armature from the North pole side of the field coil and “exits” the armature from the field coil’s South pole side.

The conductors located on the other pole are subjected to a force of the same intensity but in the opposite direction. These two opposing forces create a torque that causes the motor armature to rotate.
| Working principle of DC motor
When kept in a magnetic field, a current-carrying conductor gains torque and develops a tendency to move. In short, when electric fields and magnetic fields interact, a mechanical force arises. This is the principle on which the DC motors work. |
Edited by Lisa
Post time: Dec-03-2021